MU Extension encourages you to report precipitation
Linda Geist
Writer
Phone: 573-882-9185
Email: GeistLi@missouri.edu
University of Missouri Extension
Thursday, May 18, 2023
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Missouri farmers who check rain gauges daily can help other farmers across the nation by reporting precipitation totals.
Tony Lupo, University of Missouri professor of atmospheric science and interim MU Extension climatologist, encourages farmers to be citizen scientists by reporting daily precipitation totals to the Community Collaborative Rain, Hail and Snow network, or CoCoRaHS (pronounced KO-ko-rozz).
Through this volunteer network, backyard weather observers measure rain, hail and snow in communities in all 50 states, Canada and the Bahamas. Climatologists then compile and map the information at www.cocorahs.org. The CoCoRaHAS website gives precipitation maps in real time, in addition to historical information.
To report, go to https://www.cocorahs.org/Application.aspx. Lupo says participation is easy and free. Participants need a rain gauge and receive free, brief online training.
Lupo also recommends the Missouri Climate Center, which links to the National Drought Monitor. It gives current conditions and an outlook. The National Drought Monitor analyzes Condition Monitoring Observer Reports from citizens and others to map the severity of drought by nation, state and county.
See https://unldroughtcenter.maps.arcgis.com for these reports.
The Farm Service Agency uses these reports to help determine federal drought and flood declarations. These declarations govern what counties qualify for assistance for affected row crops, livestock, forages and specialty crops.
Lupo says the Missouri Climate Center's direct link to the National Drought Monitor has proved invaluable in recent drought years. Missourians submitted 539 reports between July 1, 2022, and Feb. 28, 2023.
Other resources to help the agricultural community:
- Midwestern Regional Climate Center (MRCC) serves the nine-state Midwest region of Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin. MRCC's easy-to-read, customizable charts include growing season statistics, frost/freeze probabilities and information on growing degree days. Go to https://mrcc.purdue.edu.
- Vegetation Impact Program (VIP), at https://mrcc.purdue.edu/VIP, monitors and assesses real-time information from MRCC on the same website. MU collaborates with other universities and agencies across the U.S. on this site. Data from VIP helps producers with frost and freeze guidance, stress degree days and the Keetch-Byram Drought Index.
- Horizon Point, offered by MU Extension at http://agebb.missouri.edu/horizonpoint, gives rainfall runoff estimators, weed and scouting aids, fall nitrogen application charts and planting-depth soil temperature, among the many offerings. Users can subscribe to receive email advisories.
- Missouri Mesonet presents information from real-time weather stations in more than 40 sites across the state. The Mesonet website gives a weather summary of precipitation, wind speed and soil temperature by station. See http://agebb.missouri.edu/weather/stations.
- Useful to Usable (U2U) provides decision tools on climate, growing degree days, split nitrogen application and crop water use in the nation's Corn Belt. MU is one of the partners. Visit https://mrcc.purdue.edu/U2U. U2U has interactive tools that farmers may find especially useful, Lupo says. The Growing Degree Day tool lets producers enter planting date and hybrid to obtain estimates of when critical events such as silking, black layer and freeze might occur. AgClimate View provides a historical view of climate and yield across the Corn Belt. Farmers can plot and compare yield data for corn and soybean over a five-year period and compare nitrogen application using variable prices and percentages.
- Missouri Climate Center, through the MU College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources, offers numerous weather and climate-related articles and resources specifically for Missouri at http://climate.missouri.edu.
Lupo says there are many other free online climate global and local resources, including these:
- National Climatic Data Center, https://www.ncei.noaa.gov
- NOAA Climate Portal, https://www.climate.gov
- Regional Climate Centers, https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/regional/regional-climate-centers
- State Climate Offices, https://stateclimate.org
- National Weather Service, https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov
Graphic available for this release:
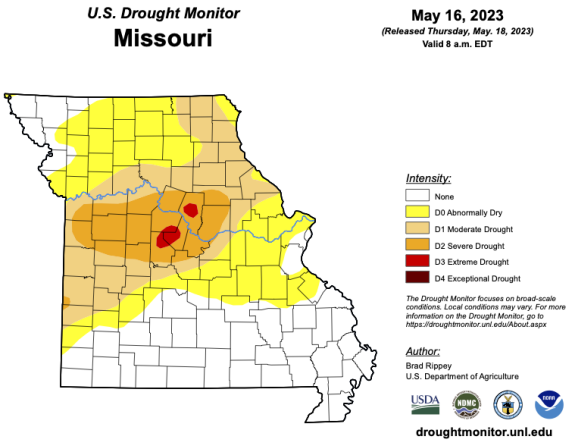
Farmers can make valuable contributions to weather reporting services by
checking rain gauges and reporting the results. Reports to the Missouri Climate Center's direct link to the National Drought Monitor have proved invaluable in
recent drought years.
Source: Tony Lupo, 573-884-1638